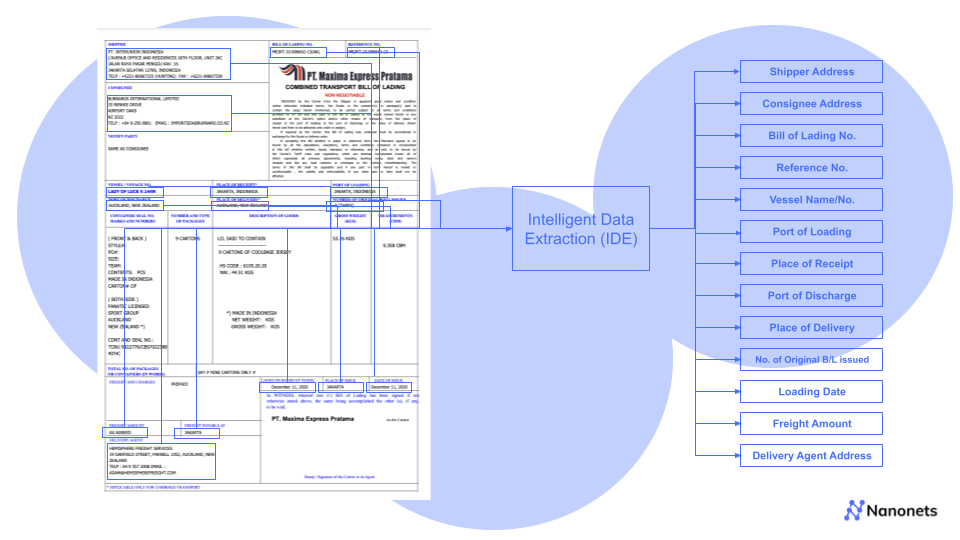
Data is the life of business operations. Organisations have vast oceans of information, from invoices and purchase orders to customer forms and legal documents.
However, the real challenge lies not in having this data, but in effectively extracting, processing, and utilising it. This is where Intelligent Data Extraction (IDE) comes into play – a revolutionary approach that’s transforming how businesses handle information.
Intelligent Data Extraction is an automated process of accurately identifying and extracting relevant data points from documents leveraging modern-day technology.
But why do we need it? Simply because, Traditional data capture methods, such as manual data entry or leveraging obsolete technology like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) have long faced numerous challenges:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Time-intensive manual entry | Employees spending countless hours typing data from physical documents into digital systems |
| Error-prone processes | Human errors in data entry leading to costly mistakes and inefficiencies |
| Bottlenecks in workflows | Slow document processing creating delays in business operations |
| Inability to handle varied document formats | Difficulty in processing diverse document types and layouts |
As businesses continue to balance these challenges with resources, the need for a more sophisticated, automated approach has become increasingly crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what Intelligent Data Extraction is and how it works, the key differences between IDE and traditional OCR and the benefits IDE brings to businesses. We will also highlight some real-world applications and use cases of IDE.
So, let’s get started on how Intelligent Data Extraction is revolutionising the way organisations handle data.
What is Intelligent Data Extraction (IDE)?
Intelligent Data Extraction refers to the automated process of identifying, extracting, and processing relevant information from various document types using advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP). Unlike traditional automated data capture methods like OCR, IDE goes beyond simply recognising text – it understands context, identifies patterns, and can adapt to different document formats and layouts.
How Intelligent Data Extraction Works
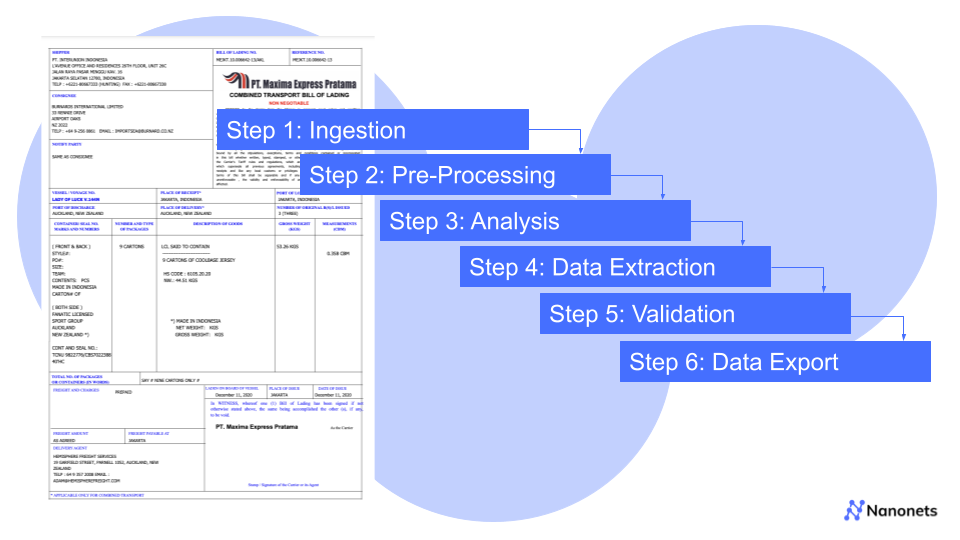
The IDE process typically involves a few pre-processing steps and once the data gets extracted, there are a few post-processing steps involved as well. Let’s take a quick comprehensive look at how IDE works:
1. Document Ingestion: The first step is where the IDE system accepts various document types. They could be PDFs, images, or even scanned documents.
2. Pre-processing: Before undergoing analysis and extraction, the documents have to be pre-processed. This can involve a few different steps such as:
- Image enhancement
- Noise reduction
- Orientation correction
- Format standardisation
3. Advanced Analysis: This is arguably the most crucial step and one where the essence of Intelligent Data Extraction lies. This step leverages advanced technologies for analysis of the ingested documents:
- Computer Vision: Identifies document structure and layout
- Machine Learning: Recognises patterns and learns from previous data extractions for similar document types
- Natural Language Processing: Understands context and relationships between data points
4. Data Extraction: In this step, based on a thorough analysis, relevant information is identified and extracted. It could involve:
- Key-value pair identification
- Table detection and data extraction
- Handwriting recognition
5. Validation and Verification: Extracted data is now checked for accuracy, it could involve multiple options such as:
- Cross-referencing with existing databases
- Automated error detection based on predefined logic
- Confidence scoring for extracted data
- Manual review
6. Data Export: Once the data has been accurately identified, extracted and verified, processed information is exported in the required format.
- Integration with existing systems (ERP, CRM, etc.)
- Structured data output (JSON, XML, CSV, etc.)
Technologies behind IDE
Three main technologies work together to make Intelligent Data Extraction both powerful and accurate.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is like the brain of IDE systems. It helps the software make smart decisions about what information to pull from documents and how to understand it.
Just as humans get better at a task with practice, AI systems improve their accuracy over time as they process more documents. This means the more you use an IDE system, the better it gets at its job.
2. Machine Learning (ML): ML brings the ability to spot patterns and adapt to different types of documents.
Some machine learning is supervised, which means the system is trained on documents it knows about – like common invoice formats.
Other learning is unsupervised, where the system figures out patterns on its own.
There’s also deep learning, which helps tackle really complex documents that might be confusing. This mix of learning styles means IDE can handle many different document types accurately.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP helps IDE systems understand written language more like a human would. Instead of just recognising words, NLP helps the system understand what those words mean in context.
It can pick out important information like names, dates, and companies, and understand how different pieces of information relate to each other. This means the system doesn’t just copy text – it understands what it’s reading.
How is IDE Different from OCR?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) has been the traditional go-to technology for digitising printed or handwritten text. While OCR has been valuable, it has significant limitations:
1. Text Recognition Only: OCR simply converts printed or handwritten text into machine-encoded text
2. Template Dependency: Template-based OCR has traditionally had limited success with different document types or layouts
3. Limited Accuracy: Struggles with varied fonts, or poor image quality
4. No Contextual Understanding: Cannot comprehend the meaning or relevance of extracted text
IDE vs. OCR: A Comparative Analysis
With a better understanding of OCR and its limitations, we can now dive into a comparative analysis between OCR and IDE, on a few parameters:
| Feature | OCR | IDE |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence Level | Basic text recognition | Advanced understanding of content, context, and relationships |
| Handling of Unstructured Data | Struggles with unstructured formats | Efficiently processes both structured and unstructured data |
| Accuracy and Error Handling | Prone to errors, especially with complex documents | Higher accuracy through AI-powered verification and learning |
| Adaptability | Requires specific templates or formats | Adapts to various document types and layouts |
| Processing Capabilities | Limited to character recognition | Extracts meaningful data, understands context, and can make decisions |
Benefits of IDE over Traditional OCR
1. Enhanced accuracy with targeted human intervention
Modern-day IDE engines can reach up to 100% accuracy in data extraction, improving over time. What is interesting is that they come with validation features in-built. They can flag a data point if it is inaccurately extracted and can notify humans for targeted intervention. Not only does this increase accuracy but also significantly cuts down time needed. According to a study by Gartner, organisations that implement intelligent document processing solutions can reduce manual data entry errors by up to 80%.
2. Increased Efficiency
This is a no-brainer. Automated data extraction processes deliver significant time-savings when compared to manual counterparts. But, the challenge with leveraging obsolete technologies like OCR, is that inaccurate data extraction can end up costing more time than manual data entry. Even with accurate extraction for standard formats, post-processing and formatting can take up a lot of time. The one-stop solution which delivers all necessary features, if you’re dealing with large volumes, is IDE. Accurate extraction with post-processing and validation features built in significantly reduces processing times, improving efficiency. A report by AIIM found that organisations using intelligent document processing solutions can reduce document processing time by up to 75%.
3. Cost Reduction
By minimising the need for manual data entry, businesses can significantly cut labor costs, while the reduced need for error correction further decreases operational expenses. Additionally, IDE engines help optimise resource allocation, allowing organisations to redirect human capital to more strategic tasks. A study by Deloitte revealed that implementing intelligent document extraction solutions can lead to cost savings of up to 30-50% in back-office operations.
4. Improved Scalability
IDE engines also offer improved scalability, seamlessly handling increasing document volumes as a business grows, adapting to new document types, and doing so without a proportional rise in costs. This ensures that businesses can scale efficiently without compromising data accuracy. According to IDC, organisations using intelligent document processing solutions can handle up to 3 times more document volume without increasing staff.
5. Better Compliance
Furthermore, IDE enhances compliance, offering consistent data extraction processes, maintaining detailed audit trails, and reducing the risk of human errors, particularly in compliance-sensitive information, thus safeguarding businesses from potential regulatory issues. A survey by AIIM found that 62% of organisations reported improved compliance and reduced risk after implementing intelligent document processing solutions.
Real-World Applications for IDE
Leveraging IDE engines can dramatically cut down on your workforce costs, especially in large enterprises processing hundreds of thousands of documents annually. Not just that, there are significant savings on error-correction costs as well, in industries where a simple data entry mistake can cost gravely.
1. Automated processing of Invoices, receipts, financial statements, tax documents, loan applications and other financial documents
Industry: Finance and Audit
💡
IDE engines can help automatically ingest any financial document, understand the context, extract relevant data points from it, format and validate it and then export it to a software of your choice.
Imagine never having to deal with thousands of invoices from vendors with varying formats and manually entering data in an excel sheet. Traditional OCR engines can help automate this to some extent but are easily thrown off by different layouts, complicated tables, multiple line-items or handwritten documents.
2. Automating patient record maintenance, insurance claim processing, or data extraction from medical forms
Industry: Healthcare
💡
Modern-day IDEs can process all medical documents, including patient forms, insurance claims, etc. in a secure, HIPAA or GDPR compliant manner.
Healthcare professionals struggle with lots of paperwork. Digitizing patient records, filing insurance claims or simply extracting data from medical forms are all instances of mundane data entry scenarios that take time and attention away from patient care. Due to the sensitive nature of the data involved in this industry, traditional OCR engines just don’t cut it. That’s where modern-day IDE engines come in. Not only can they help automate data extraction from any healthcare document, but they also come with advanced security features, like, HIPAA compliance, GDPR compliance, ISO and SoC certification, etc.
3. Automating contract analysis, lease abstraction, compliance and other legal document handling
Industry: Legal
💡
Legal industry usually has multi-page legal documents. IDEs are efficient at summarising or creating abstracts void of legal jargon for quick references.
Lawyers often have to refer to contracts, leases, compliance documents among others at a moment’s notice. They don’t have time to sift through multi-page legal documents, battle jargon and abbreviations, in order to get the answer they need. IDE engines, powered by LLMs now, are efficient at creating summaries containing relevant data points only. This functionality can come in handy.
4. Automating resume parsing, employee document processing and other HR functions
Industry: Human Resources
💡
Another application of IDEs is resume parsing which is a fundamental process within the HR industry. IDEs can streamline data extraction and cross-matching against external databases for increasing efficiency in talent acquisition processes.
Human resource management is another fundamental function within any organization, but one that faces operational inefficiencies due to the involved paperwork. Think of the talent acquisition vertical dealing with hundreds of resumes for candidates. Instead of manually sifting through each resume, one can deploy an IDE which screens resumes against a list of skills for a particular job description. The same goes for employee onboarding processes and other paper-heavy HR functions.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, Intelligent Data Extraction (IDE) is a significant leap forward from traditional OCR technology. In a time, where data is increasingly valuable and volumes continue to grow, IDE offers organisations a powerful tool to efficiently and accurately process their document-based information.
The benefits of IDE are clear:
Dramatically improved accuracy
Significant time and cost savings
Enhanced scalability and adaptability
Better compliance and reduced risks
As businesses continue to optimise their operations, IDE will play an increasingly crucial role in their data management strategies. The technology’s ability to understand context, learn from experience, and process complex, unstructured data makes it an invaluable asset for organisations across industries.
Looking ahead, we can expect IDE technology to continue evolving, with advancements in AI and machine learning driving even greater capabilities.
The future of data extraction is intelligent, and that future is here today.